Best Standard Deviation Calculator Online 2025
Standard Deviation Calculator
Chart Visualization
Standard deviation calculator is one of the most essential concepts in statistics, data analysis, finance, research, and many other fields. It provides a measure of how spread out the values in a data set are. Understanding the variation or dispersion of data points is crucial for decision-making, predicting trends, and analyzing performance.
Whether you are a student, teacher, researcher, analyst, or business professional, having a reliable tool to calculate standard deviation can save time and increase accuracy. Our Standard Deviation Calculator allows users to instantly calculate population and sample standard deviations, mean, variance, and visualize data with graphs, making it an indispensable tool for beginners and professionals alike.
This guide will cover:
- What standard deviation is
- The difference between population and sample standard deviation
- Formulas and manual calculation steps
- Real-life applications
- Benefits of using an online calculator
- How our Standard Deviation Calculator works
- Frequently Asked Questions
By the end of this guide, readers will not only understand standard deviation but also know how to calculate it quickly and efficiently using our online tool. You can also use our random number generator tool.
What is Standard Deviation?
Standard deviation measures the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values. In simpler terms, it tells us how much the individual numbers in a data set deviate from the mean (average).

Key Points:
- Low standard deviation: Values are close to the mean; data is consistent.
- High standard deviation: Values are spread out; data has more variation.
Example:
Consider two sets of numbers:
Data Set A: 49, 50, 51
Data Set B: 10, 50, 90
Both sets may have similar averages, but Data Set B has numbers spread further from the mean, resulting in a higher standard deviation. This demonstrates why standard deviation is a better measure of variability than the mean alone.
Importance of Standard Deviation
Standard deviation is widely used across different disciplines and industries. It is a key statistical tool for analyzing consistency, reliability, and risk.
Applications:
- Education: Measure student performance consistency.
- Business: Analyze sales trends and performance fluctuations.
- Finance: Assess risk and volatility in investments.
- Healthcare: Evaluate variability in clinical trials and patient outcomes.
- Sports: Assess player performance consistency.
- Manufacturing: Monitor quality control and production consistency.
By understanding the spread of data, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions, plan strategies, and predict outcomes more accurately.
Types of Standard Deviation
There are two main types of standard deviation:
- Population Standard Deviation (σ)
Population standard deviation is used when the data set represents the entire population. The formula divides by the total number of values, N.
Example: Examining all students’ scores in a school where all scores are available.
- Sample Standard Deviation (s)
Sample standard deviation is used when the data set represents a sample from a larger population. The formula divides by (n−1) to account for sampling bias.
Example: Analyzing scores of 20 students randomly selected from a class of 500.
Understanding the difference is important because using the wrong formula can lead to inaccurate results.
Standard Deviation Formulas
Population Standard Deviation Formula:

Sample Standard Deviation Formula:
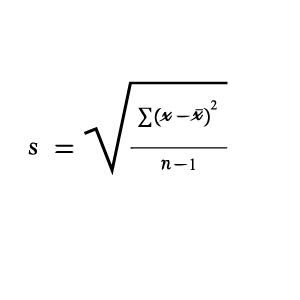
Where:
- x = each individual value
- μ / x̄ = mean
- N = population size
- n = sample size
- Σ = summation
Step-by-Step Calculation
Let’s take a sample data set: 10, 20, 30, 40
1. Calculate Mean:
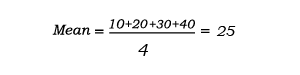
2. Calculate Deviations from Mean:
- 10 − 25 = −15
- 20 − 25 = −5
- 30 − 25 = 5
- 40 − 25 = 15
3. Square Deviations:
- (−15)² = 225
- (−5)² = 25
- 5² = 25
- 15² = 225
4. Sum of Squared Deviations:
- 225 + 25 + 25 + 225 = 500
5. Variance:
- Population variance = 500 / 4 = 125
- Sample variance = 500 / 3 = 166.67
6. Standard Deviation:
- Population SD = √125 ≈ 11.18
- Sample SD = √166.67 ≈ 12.91
Manual calculations can be tedious for larger data sets. Our Standard Deviation Calculator automates this process and produces accurate results instantly.
How Our Standard Deviation Calculator Works
Our online tool is designed to simplify calculations while providing educational value. Users can:
1. Enter numbers separated by commas
2. Choose population or sample standard deviation
3. Click the calculate button
4. View results instantly:
- Count (N)
- Mean
- Variance
- Population SD
- Sample SD
- Step-by-step explanation
- Graphical visualization of deviations
Additional features include:
- Copy results button for easy sharing
- Export CSV for further analysis
- Toggleable step-by-step breakdown
- Responsive design for desktop and mobile devices
- Error validation to ensure accurate inputs
The calculator is suitable for students, researchers, analysts, and professionals in any field dealing with numerical data.
Benefits of Using Our Calculator
- Fast & Accurate: Instantly calculate SD without manual errors
- User-Friendly: No need to understand formulas for beginners
- Visual Representation: Bar chart shows deviations visually
- Data Export: Copy or export results to CSV or Excel
- Free & Online: No sign-up required, use anywhere, anytime
- Step-by-Step Learning: Understand the process, not just the result
These benefits make our calculator not just a tool but also an educational aid for learning statistics.
Real-Life Applications
Education:
Teachers and students can analyze test scores to determine consistency in student performance.
Business & Sales:
Companies can analyze sales trends, measure consistency, and identify fluctuations to make informed decisions.
Finance & Investment:
Investors use standard deviation to measure market volatility and manage portfolio risks.
Healthcare:
Researchers analyze clinical trial data to assess variability and determine the reliability of results.
Sports Analytics:
Sports coaches can measure player performance consistency over time to optimize training.
Manufacturing:
Standard deviation helps monitor product quality and detect inconsistencies in production.
Comparison Between Population and Sample SD
| Feature | Population SD (σ) | Sample SD (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | σ | s |
| Data | Full population | Sample |
| Denominator | N | n−1 |
| Use Case | Complete dataset | Partial dataset |
Choosing the correct type ensures accuracy in analysis.
Advantages of Standard Deviation
- Easy to interpret and compare data
- Accounts for every data point
- Provides reliable measure of spread
- Complements mean and variance analysis
- Widely accepted in research and industry
Limitations of Standard Deviation
- Sensitive to extreme values or outliers
- Not ideal for highly skewed data
- Requires numerical data inputs
- Does not indicate the direction of data deviation
Standard Deviation vs Variance
| Basis | Standard Deviation | Variance |
|---|---|---|
| Unit | Same as original data | Squared units |
| Interpretability | Easy to understand | Harder for beginners |
| Calculation | Square root of variance | Sum of squared deviations / N or n−1 |
Tips for Beginners
- Avoid rounding numbers too early
- Use sample SD if unsure about dataset completeness
- Compare SDs of similar types of data
- Use visualizations for better understanding
Why Use Our Standard Deviation Calculator?
Our calculator is more than just a tool:
- Step-by-step explanations make learning statistics easier
- Graphical visualization helps understand deviations instantly
- Copy/export features make it professional-grade
- Mobile-friendly design ensures usability anywhere
- Fast and accurate results save time and reduce errors
Compared to traditional tools, our calculator provides accuracy, visual insight, and educational value all in one platform.
FAQs
Conclusion
Standard deviation is a fundamental concept that helps measure variability, analyze trends, and make informed decisions. Calculating it manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
Our Standard Deviation Calculator offers:
- Instant results
- Step-by-step calculation
- Population & sample options
- Graphical visualization
- Copy/export functionality
- Beginner-friendly interface
It is suitable for students, professionals, researchers, analysts, and anyone working with numerical data. Use it to quickly analyze your datasets, understand trends, and make data-driven decisions with confidence.






One Comment